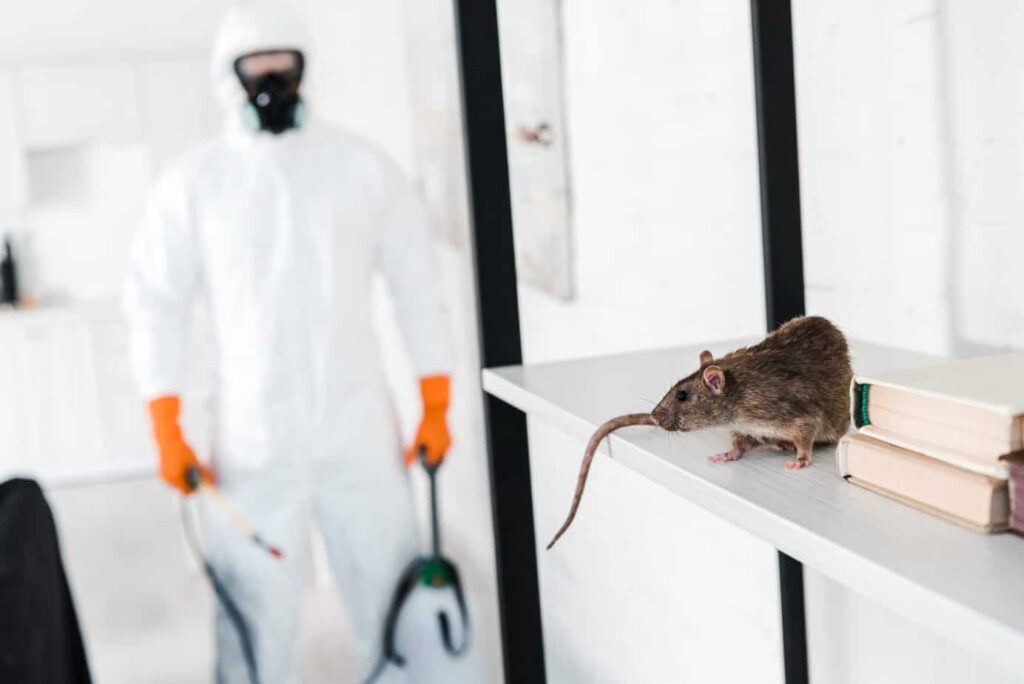
Rodents, stealthy and persistent, can infiltrate homes, businesses, and public spaces, posing significant health and safety risks. Addressing rodent infestations promptly and effectively is paramount in maintaining a pest-free environment. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of rodent control, exploring various methods and strategies to combat these elusive creatures to get Pest Control San Diego.
Understanding Rodents
Before devising control measures, it’s crucial to comprehend the biology, behavior, and species diversity of rodents. Identifying signs of infestation and understanding their habits aids in implementing targeted control strategies.
Common Species of Rodents
Rodents encompass a diverse group of species, with three main culprits infesting urban and suburban environments:
- House Mice (Mus musculus): Small and adaptable, house mice are prolific breeders and prolific chewers, capable of causing extensive damage to property and transmitting diseases.
- Norway Rats (Rattus norvegicus): Also known as brown rats, Norway rats are larger and more aggressive than house mice, often found in sewers, basements, and commercial buildings.
- Roof Rats (Rattus rattus): Agile climbers, roof rats inhabit attics, trees, and elevated areas, posing a threat to both indoor and outdoor spaces with their gnawing and nesting behaviors.
Biology and Behavior
Understanding the reproductive cycles, nesting habits, and movement patterns of rodents is essential in devising effective control measures.
- Reproduction and Lifespan: Rodents reproduce rapidly, with a single pair capable of producing hundreds of offspring in a year. Their short gestation period and high fertility rate contribute to population explosions in infested areas.
- Nesting and Feeding Habits: Rodents seek shelter in secluded areas such as wall voids, attics, and burrows, where they construct nests from readily available materials. Their omnivorous diet includes grains, seeds, fruits, and even insects, making food sources abundant in both urban and rural settings.
- Movement Patterns: Rodents are nocturnal creatures, preferring to forage and explore under the cover of darkness. They navigate through narrow openings, utilizing established runways and pathways to access food, water, and shelter.
Identification of Rodent Infestations
Recognizing the signs of rodent activity and understanding common entry points and environmental factors are crucial steps in controlling infestations.
- Signs of Activity: Indicators of rodent infestations include droppings, gnaw marks, grease smudges along walls, and evidence of nesting materials such as shredded paper or fabric.
- Common Entry Points: Rodents exploit openings as small as a quarter inch to gain access to structures, including gaps around utility pipes, vents, and foundation cracks. Identifying and sealing entry points is essential in preventing infestations.
- Environmental Factors: Factors such as food availability, habitat suitability, and proximity to water sources influence rodent populations. Addressing these environmental conditions mitigates the risk of infestations and facilitates long-term control.
Effective Rodent Control Methods
Combatting rodent infestations requires a multifaceted approach, incorporating exclusion techniques, sanitation practices, and chemical or biological control methods.
Exclusion Techniques
Preventing rodent entry through physical barriers and structural modifications is a cornerstone of effective control efforts.
- Sealing Entry Points: Thoroughly inspecting structures for gaps, cracks, and openings and sealing them with durable materials such as steel wool, hardware cloth, or caulk prevents rodents from gaining access indoors.
- Installing Rodent-Proofing Materials: Installing door sweeps, mesh screens, and vent covers deters rodents from entering through vulnerable points such as doors, windows, and vents.
- Implementing Physical Barriers: Creating barriers such as gravel or concrete strips around foundations, elevating storage units, and trimming vegetation reduces rodent access to buildings and nesting sites.
Sanitation and Habitat Modification
Removing food sources, eliminating harborage areas, and implementing proper waste management practices reduce the attractiveness of properties to rodents.
- Removing Food Sources: Properly storing food in airtight containers, cleaning up spills and crumbs promptly, and securing garbage bins minimizes food availability and discourages rodent foraging.
- Eliminating Nesting Sites: Decluttering storage areas, maintaining landscaping, and removing debris from yards and outdoor spaces deprive rodents of shelter and nesting materials.
- Proper Waste Management: Regularly emptying trash bins, sealing garbage bags tightly, and disposing of organic waste promptly reduce odors and attractants that lure rodents to properties.
Chemical and Biological Control
Utilizing rodenticides, traps, and biological control agents effectively reduces rodent populations and prevents infestations from escalating.
- Rodenticides: Baits containing anticoagulant or acute toxicants are effective in controlling rodent populations when placed strategically in areas of high activity. However, careful handling and placement are essential to minimize risks to non-target species.
- Traps and Baits: Snap traps, glue boards, and electronic traps offer humane and targeted control options for capturing and killing rodents. Proper placement and baiting increase the effectiveness of trapping efforts.
- Biological Control Agents: Predatory species such as barn owls, cats, and certain snake species naturally prey on rodents, helping to keep populations in check. Encouraging the presence of these natural predators through habitat enhancements supports sustainable rodent control.
Prevention Strategies
Adopting proactive measures, fostering community awareness, and seeking professional assistance are key components of long-term rodent management.
Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Conducting routine inspections, implementing repairs, and utilizing monitoring devices help detect and prevent rodent infestations before they escalate.
- Routine Property Checks: Regularly inspecting buildings, storage areas, and outdoor spaces for signs of rodent activity allows for early intervention and targeted control measures.
- Repairs and Maintenance: Addressing structural deficiencies, repairing damaged screens, and reinforcing entry points prevents rodents from gaining access to buildings and nesting sites.
- Monitoring Devices: Installing rodent monitoring devices such as bait stations, motion-activated cameras, and tracking powders aids in assessing the severity of infestations and evaluating control measures’ effectiveness.
Education and Awareness
Educating residents, employees, and community members about rodent behavior, prevention strategies, and the importance of early intervention fosters a collaborative approach to rodent control.
- Understanding Rodent Behavior: Providing information on rodent biology, habits, and identification empowers individuals to recognize and address infestations proactively.
- Educating Residents and Employees: Offering training sessions, distributing informational materials, and promoting good sanitation practices raise awareness about rodent control and prevention measures.
- Community Engagement: Collaborating with local authorities, neighborhood associations, and businesses to implement community-wide rodent control initiatives promotes shared responsibility and accountability for maintaining rodent-free environments.
Professional Pest Control Services
Engaging the services of pest control professionals equipped with expertise, resources, and integrated pest management strategies ensures comprehensive and sustainable rodent control.
- Integrated Pest Management: Pest control professionals employ a holistic approach to rodent management, combining preventive measures, monitoring, and targeted interventions to address infestations effectively.
- Customized Treatment Plans: Tailoring control strategies to specific properties, environments, and infestation levels maximizes effectiveness and minimizes environmental impacts and risks to non-target species.
- Follow-Up and Monitoring: Regular follow-up inspections, maintenance visits, and monitoring efforts ensure the long-term success of rodent control programs, allowing for adjustments and refinements as needed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective rodent control requires a proactive and integrated approach that addresses the underlying causes of infestations while employing a combination of exclusion, sanitation, and control measures. By understanding rodent behavior, implementing preventive strategies, and seeking professional assistance when needed, property owners and managers can safeguard their homes, businesses, and communities from the threats posed by these resilient pests. Consistency and vigilance are key in the ongoing effort to achieve and maintain rodent-free environments.