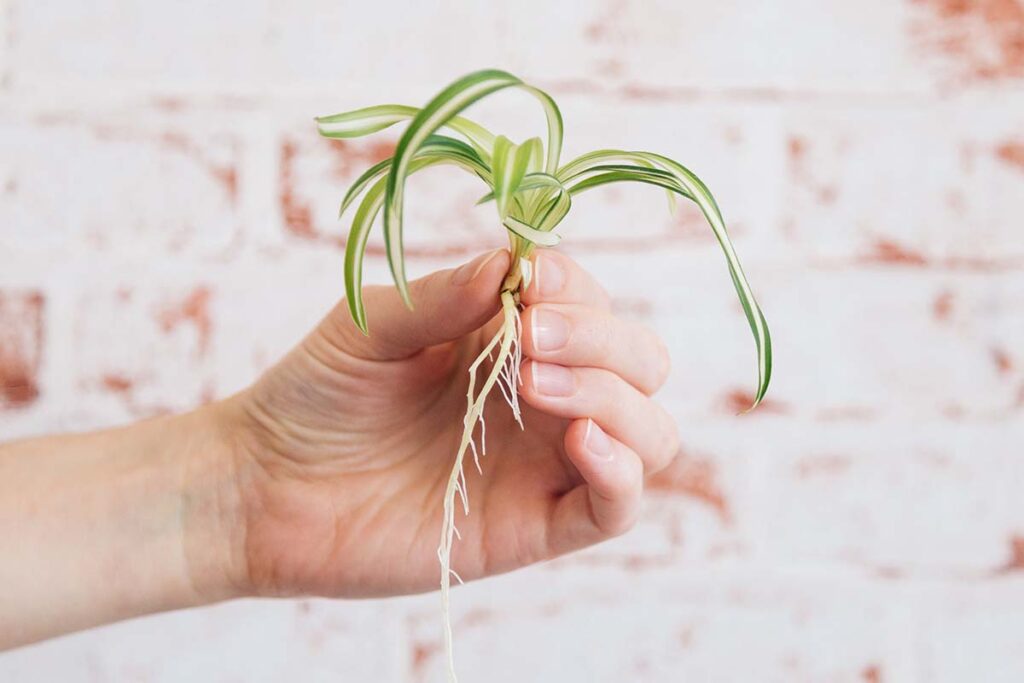
Spider plants, known for their graceful foliage and ease of care, are beloved additions to indoor and outdoor spaces alike. One of the most intriguing aspects of these plants is their ability to reproduce through “baby” spider plants, or plantlets, which emerge from the parent plant. In this article, we explore the timeline of baby spider plant growth, from germination to maturity, and discuss the factors that influence their development.
**I. Introduction**
Spider plants, with their arching leaves and striking appearance, have long captivated plant enthusiasts with their unique charm. Among the many attributes that make them popular, their ability to produce “babies” or plantlets is particularly fascinating. These miniature versions of the parent plant emerge from long stems, dangling delicately like spider legs, hence the name. Understanding the growth process of these baby spider plants is essential for both novice and experienced gardeners alike.
**II. Germination and Development**
*Germination Process*
1. **Seed Preparation**: Before germination can occur, spider plant seeds require suitable conditions to break dormancy and initiate growth. Proper seed handling, including scarification or soaking, can help expedite the germination process.
2. **Environmental Conditions**: Germination success is heavily influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, and light. Providing optimal conditions, such as warm temperatures and consistent moisture, encourages seed viability and germination.
*Growth Stages of Baby Spider Plants*
1. **Seedling Stage**: Once germination occurs, spider plant seeds give rise to tiny seedlings that gradually develop roots and leaves. During this stage, seedlings are vulnerable to environmental stressors and require careful monitoring and care.
2. **Maturation and Pupation**: As seedlings mature, they transition into juvenile plants and begin producing plantlets or “babies” of their own. This stage marks the culmination of the growth process and sets the stage for propagation and expansion of the spider plant population.
**III. Timeline of Baby Spider Plant Growth**
*Initial Growth Phase*
1. **Emergence of Shoots**: Within a few weeks of germination, spider plant seedlings begin to develop shoots and establish themselves in their growing environment. The emergence of new growth signals the start of the vegetative phase.
2. **Establishment of Roots**: Concurrent with shoot development, spider plant seedlings extend their root systems into the surrounding soil or growing medium. Strong, healthy roots are essential for nutrient uptake and overall plant health.
*Vegetative Growth Stage*
1. **Leaf Development**: As spider plant seedlings continue to grow, they produce an increasing number of leaves, which contribute to photosynthesis and energy production. The lush foliage characteristic of spider plants begins to take shape during this stage.
2. **Formation of Plantlets**: In addition to leaf growth, spider plant seedlings also initiate the formation of plantlets or “babies” along specialized stems called stolons. These miniature replicas of the parent plant eventually develop into independent individuals.
*Maturation and Propagation*
1. **Development of Mature Plantlets**: Over time, the plantlets produced by spider plant seedlings mature and develop roots of their own, becoming self-sustaining individuals. This maturation process varies depending on environmental conditions and care practices.
2. **Propagation Methods**: Once mature, spider plant plantlets can be harvested and propagated through various methods, including planting directly in soil or water, or by rooting in a separate container. This allows for the expansion of the spider plant collection and sharing with fellow enthusiasts.
**IV. Environmental Influences on Growth Rate**
*Light Requirements*
1. **Optimal Light Conditions**: Spider plants thrive in bright, indirect light, although they can tolerate lower light levels. Providing adequate light ensures robust growth and vibrant foliage coloration.
2. **Effects of Insufficient Light**: Inadequate light can result in leggy growth, pale foliage, and reduced plant vigor. Supplemental lighting may be necessary in low-light environments to support healthy growth.
*Temperature and Humidity*
1. **Temperature Tolerance**: Spider plants prefer moderate temperatures ranging from 65 to 75°F (18 to 24°C) but can tolerate slightly cooler or warmer conditions. Extreme temperatures can stress plants and affect growth rates.
2. **Impact of Humidity Levels**: While spider plants can adapt to a range of humidity levels, they thrive in moderately humid environments. Dry air can lead to leaf browning and tip dieback, while excessive humidity can promote fungal diseases.
*Soil and Watering Practices*
1. **Soil Composition**: Spider plants prefer well-draining soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH. A lightweight potting mix formulated for houseplants provides the ideal growing medium.
2. **Watering Frequency and Method**: Spider plants prefer consistently moist but not waterlogged soil. Allow the soil to dry slightly between waterings to prevent root rot, and avoid overhead watering, which can lead to fungal issues.
**V. Tips for Encouraging Healthy Growth**
*Providing Adequate Care*
1. **Proper Watering Techniques**: Water spider plants consistently, ensuring that the soil remains evenly moist but not waterlogged. Allow excess water to drain away to prevent root rot.
2. **Fertilization and Nutrient Needs**: Feed spider plants regularly during the growing season with a balanced liquid fertilizer formulated for houseplants. Avoid overfertilization, which can lead to salt buildup and leaf burn.
*Monitoring Growth Progress*
1. **Regular Inspection**: Monitor spider plants regularly for signs of growth and development, including new leaf emergence and plantlet formation. Address any issues promptly to prevent problems from worsening.
2. **Adjusting Care Practices**: Adjust care practices as needed based on
the plant’s response to environmental conditions. Pay attention to factors such as light exposure, temperature, and humidity levels, and make necessary modifications to optimize growth.
*Patience and Persistence*
1. **Understanding Growth Dynamics**: Recognize that growth rates may vary depending on factors such as genetics, environmental conditions, and care practices. Exercise patience and allow plants to grow at their own pace.
2. **Celebrating Milestones**: Celebrate the milestones achieved along the journey of baby spider plant growth, from the emergence of the first shoot to the maturation of plantlets. Each stage represents progress and success in nurturing healthy, thriving plants.
In conclusion, the journey of baby spider plant growth is a fascinating process that unfolds over time, influenced by a myriad of environmental factors and care practices. By understanding the timeline of growth, from germination to maturation, and implementing appropriate care techniques, gardeners can foster healthy and robust plants that bring beauty and vitality to indoor and outdoor spaces alike. With patience, persistence, and a bit of green-thumb know-how, anyone can enjoy the rewarding experience of nurturing baby spider plants to maturity.