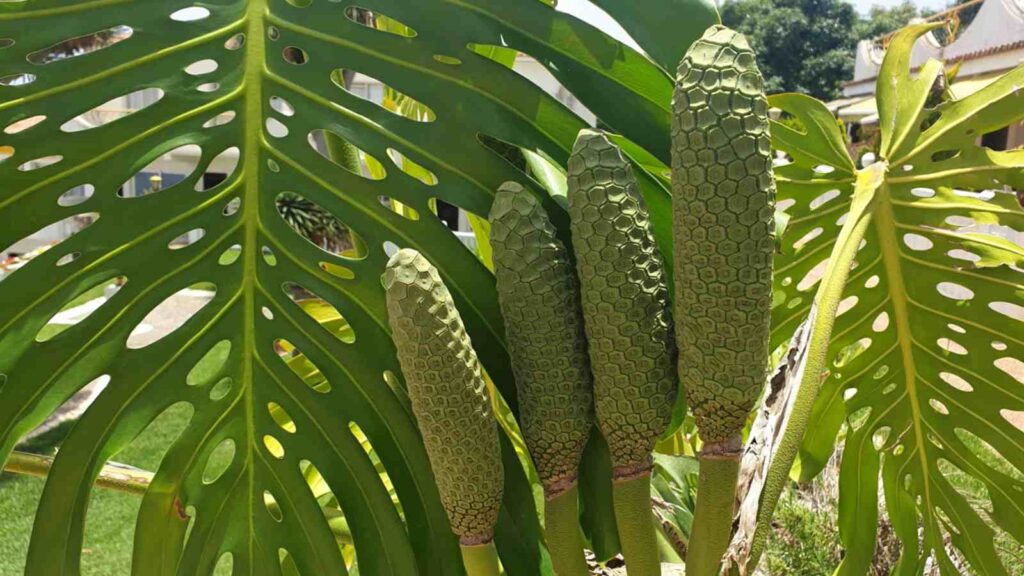
Monstera plants, with their distinctive perforated leaves and tropical allure, have become a staple in many indoor gardens. Yet, while their foliage captivates, it’s the prospect of fruiting that truly elevates the Monstera cultivation experience. Indoor gardeners often embark on a quest to coax their Monstera plants into bearing fruit, but it’s not without its challenges. In this guide, we delve into the intricacies of offering insights and techniques to unlock the fruiting potential of your indoor Monstera.
I. Introduction
Monstera plants, native to the rainforests of Central and South America, have earned a reputation for their striking appearance and ease of care. Their large, glossy leaves, adorned with characteristic splits and holes, make them a sought-after addition to any indoor jungle. However, beyond their ornamental appeal, the prospect of fruiting adds an exciting dimension to Monstera cultivation. Indoor gardeners aspire to witness the transformation of their beloved plants into fruit-bearing specimens, yet achieving this feat presents its own set of hurdles.
II. Understanding Monstera Fruit Formation
Before delving into cultivation techniques, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of Monstera fruit formation. Like all plants, Monstera undergoes a life cycle that culminates in the production of flowers and fruits. Understanding the factors that influence this process, such as light, temperature, and humidity, is key to fostering optimal conditions for fruit development.
III. Cultivation Techniques to Encourage Fruiting
Creating an environment conducive to fruiting requires careful attention to various factors, starting with lighting conditions. While Monstera thrives in bright, indirect sunlight, direct exposure can scorch its delicate foliage. Supplemental lighting options, such as grow lights, provide a solution for indoor growers lacking sufficient natural light.
Maintaining the right temperature and humidity levels is equally critical for encouraging fruiting in Monstera plants. These tropical beauties prefer warm, humid conditions reminiscent of their native habitat. Indoor growers can achieve this by maintaining temperatures within the ideal range and employing methods such as misting or using a humidity tray to elevate humidity levels.
Pruning and maintenance also play a crucial role in promoting fruiting. Removing dead or damaged foliage not only enhances the plant’s aesthetic appeal but also redirects its energy towards fruit production. Additionally, strategic pruning techniques, such as tip pruning to encourage branching, can stimulate growth and increase the likelihood of fruit formation.
IV. Pollination Methods for Indoor Monstera Plants
In their natural habitat, Monstera plants rely on pollinators such as insects and birds to facilitate fertilization. However, in indoor settings, the absence of these natural pollinators necessitates alternative methods to ensure fruit set. While some growers may opt to mimic outdoor conditions by introducing pollinating insects into their indoor garden, others may choose to take matters into their own hands through hand pollination techniques.
Hand pollination involves transferring pollen from the male to the female flowers manually. This can be accomplished using tools such as a small brush or cotton swab to collect and transfer pollen. Timing is crucial, as Monstera flowers are only receptive to pollen for a limited period. By mastering the art of hand pollination, indoor growers can increase their chances of successful fruit development.
V. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite their best efforts, indoor gardeners may encounter obstacles on the path to Monstera fruiting success. One common issue is the lack of fruiting despite providing optimal growing conditions. In such cases, growers should carefully assess environmental factors such as light, temperature, and humidity to identify any discrepancies that may be inhibiting fruit development. Adjusting cultivation techniques accordingly can help rectify these issues and encourage fruiting.
Pest and disease infestations can also hinder fruit production in Monstera plants. Common pests such as spider mites or scale insects can wreak havoc on foliage, depriving the plant of vital nutrients and energy needed for fruiting. Similarly, fungal diseases such as root rot can compromise the plant’s overall health and diminish its ability to produce fruits. Implementing preventive measures such as regular inspection and proper sanitation can help mitigate these risks and ensure a healthy, fruit-bearing Monstera plant.
In conclusion, while getting Monstera to fruit indoors may pose certain challenges, armed with the right knowledge and techniques, indoor gardeners can turn their botanical aspirations into reality. By understanding the intricacies of Monstera fruit formation, implementing cultivation techniques tailored to its needs, and addressing any issues that arise along the way, growers can unlock the fruiting potential of their beloved Monstera plants, transforming their indoor spaces into lush, tropical havens.